A study of comments on video materials posted in February 2025 on Belarusian democratic YouTube channels revealed a large-scale coordinated network of bots systematically influencing public opinion.
The analysis processed 85,736 comments on 1,132 videos left by 32,326 unique authors. Among them, 2,845 accounts were identified as having left 5 or more comments, of which 201 accounts were identified as potential bots based on behavioral indicators.
Network Structure
Analysis of connections between bots revealed a clear cluster structure with several distinct communities.
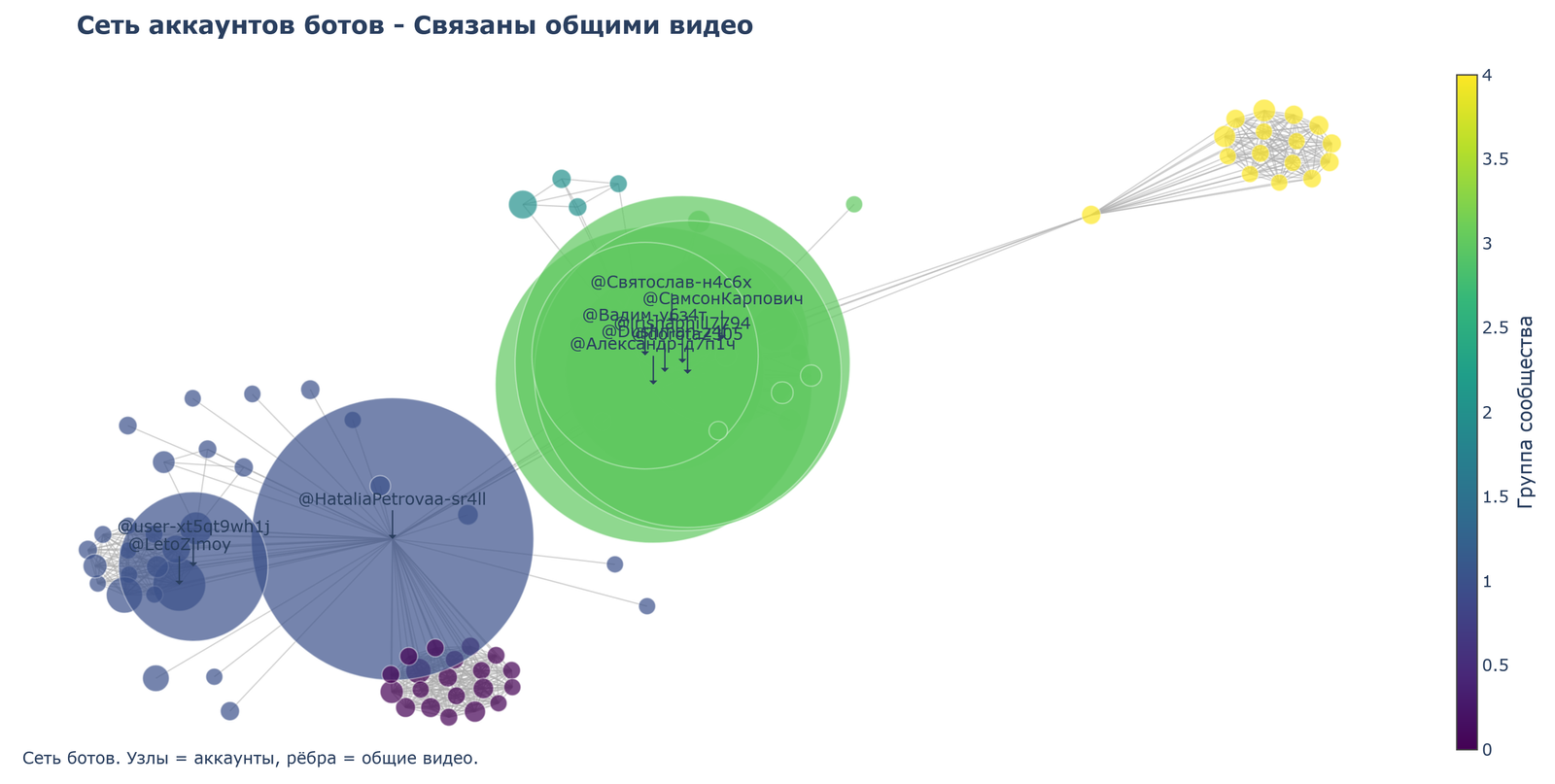
The network visualization demonstrates at least four well-defined clusters (blue, green, yellow, and purple) that function as coordinated groups commenting on the same videos. Key accounts occupying central positions in the network are distributed among clusters. In the blue cluster, accounts such as @NataliaPetrovaa-sr4ll, @user-xt5zt9whLj, and @Leto2jmoy stand out. In the green cluster, @Святослав-n4c6x, @СвмсонКарпович, @Вадим-yb34lj, @PiterFan117j94, and @Александр-j47t1c play central roles.
More detailed analysis revealed 5 functional bot clusters with different roles.

Cluster 0, with 4 participants, represents “wide-reach bots” with high indicators of comment quantity and number of commented videos.
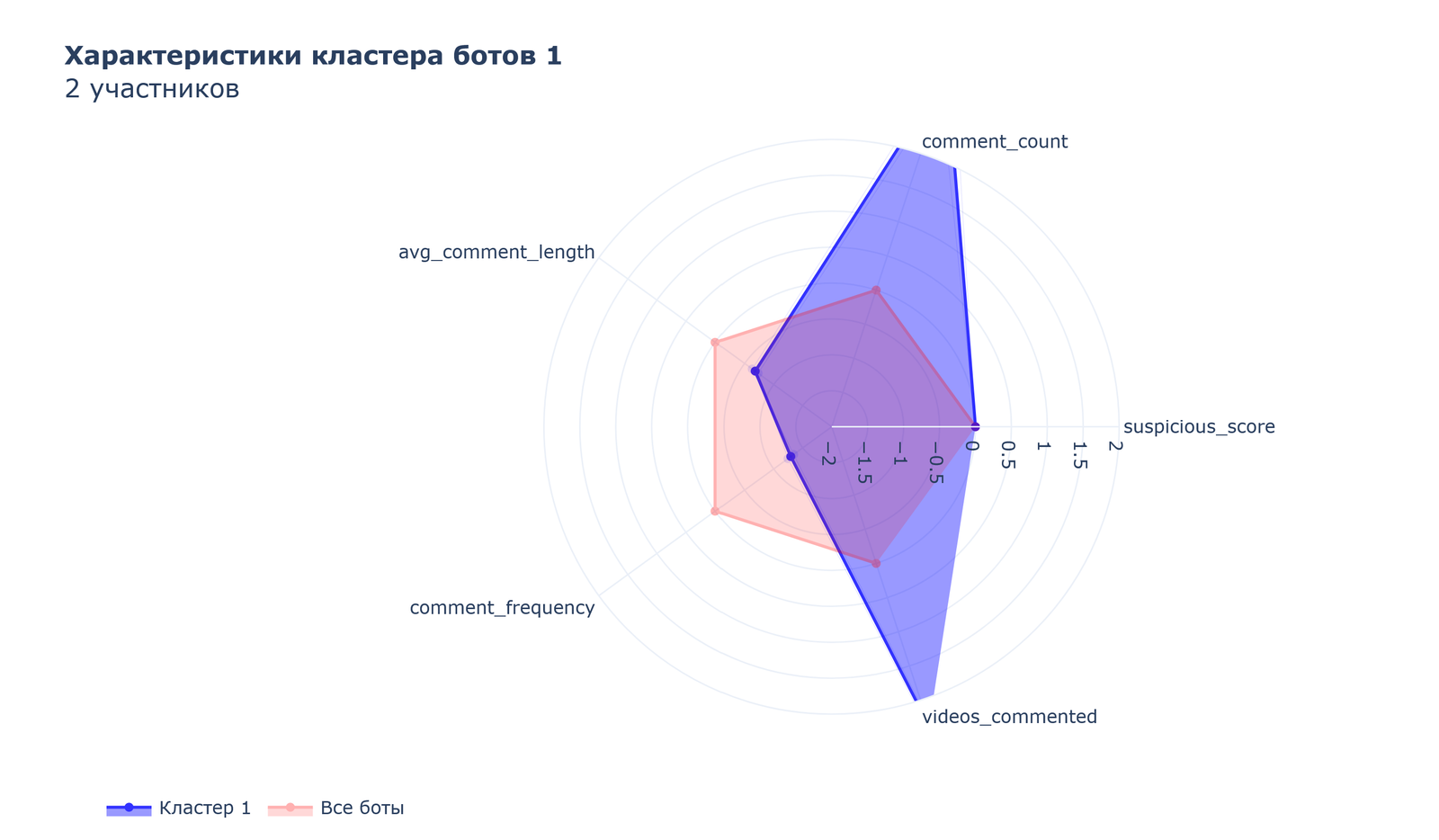
Cluster 1 includes 2 participants and functions as a group of “scouts” focused on maximum coverage of different videos with fewer comments on each.
The most numerous is Cluster 2, uniting 182 participants.
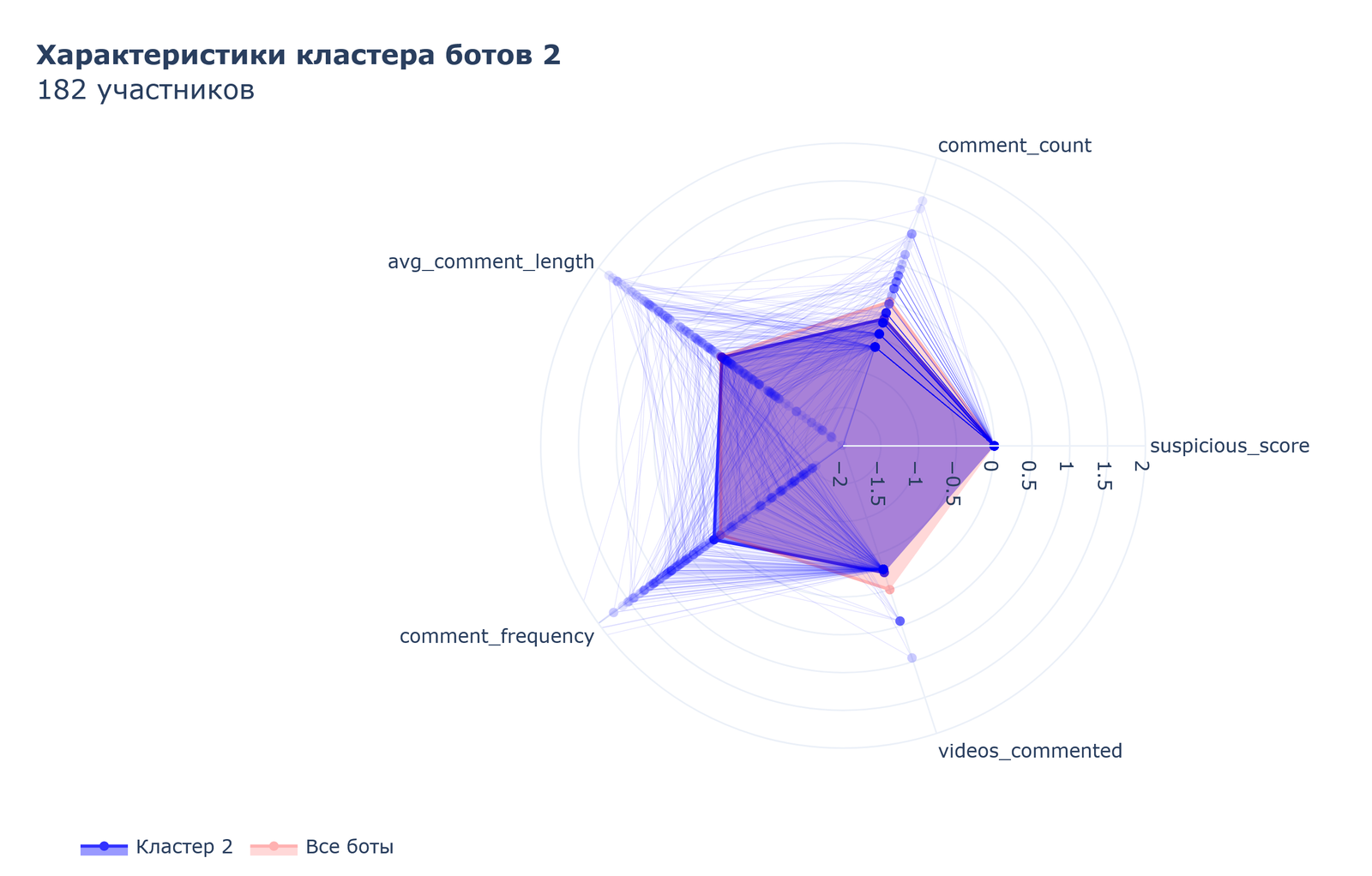
These bots act as “content generators” with very high average comment length and commenting frequency.
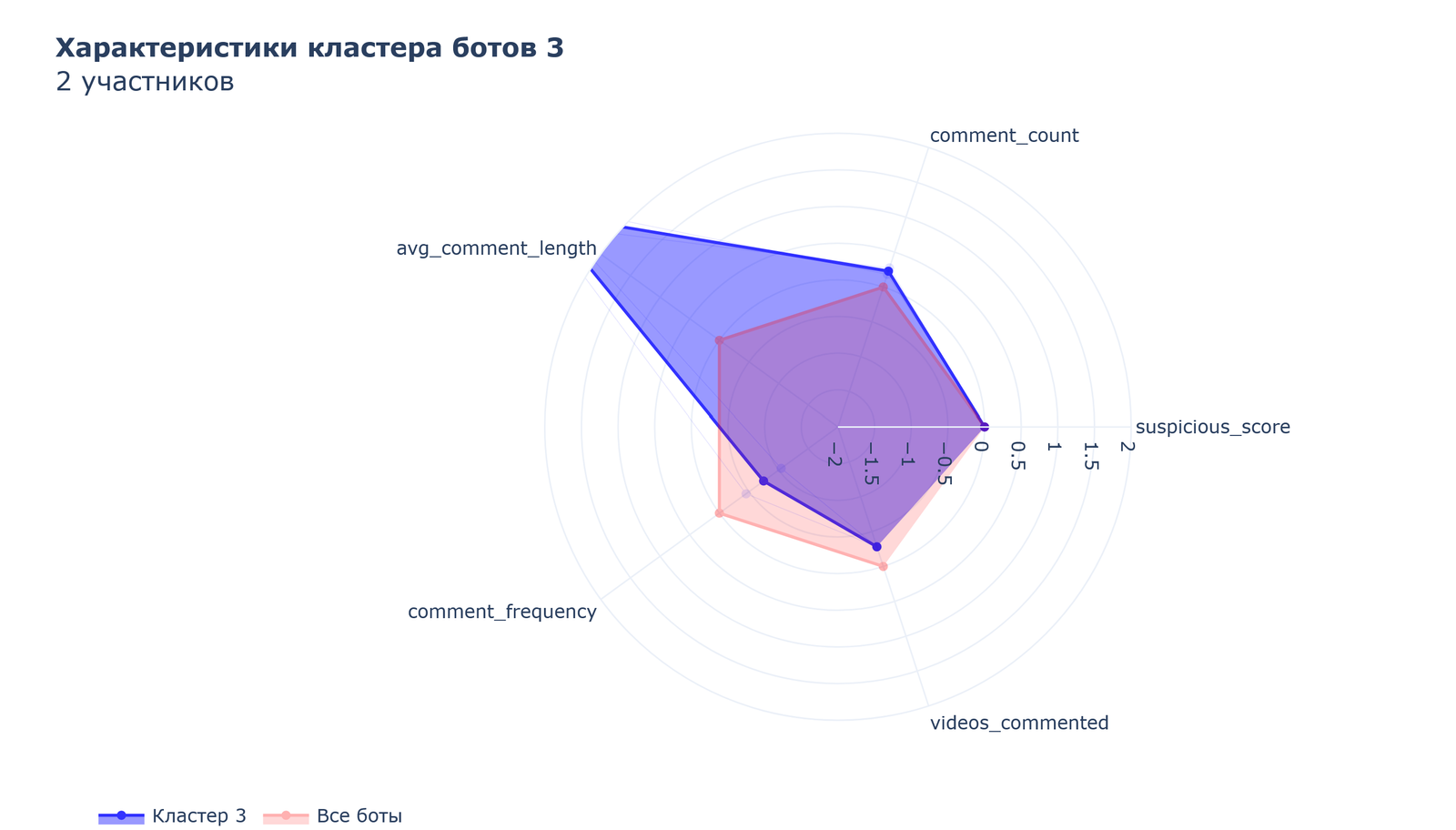
Cluster 3, which includes 2 participants, specializes in the role of “analysts” creating very long, detailed comments.
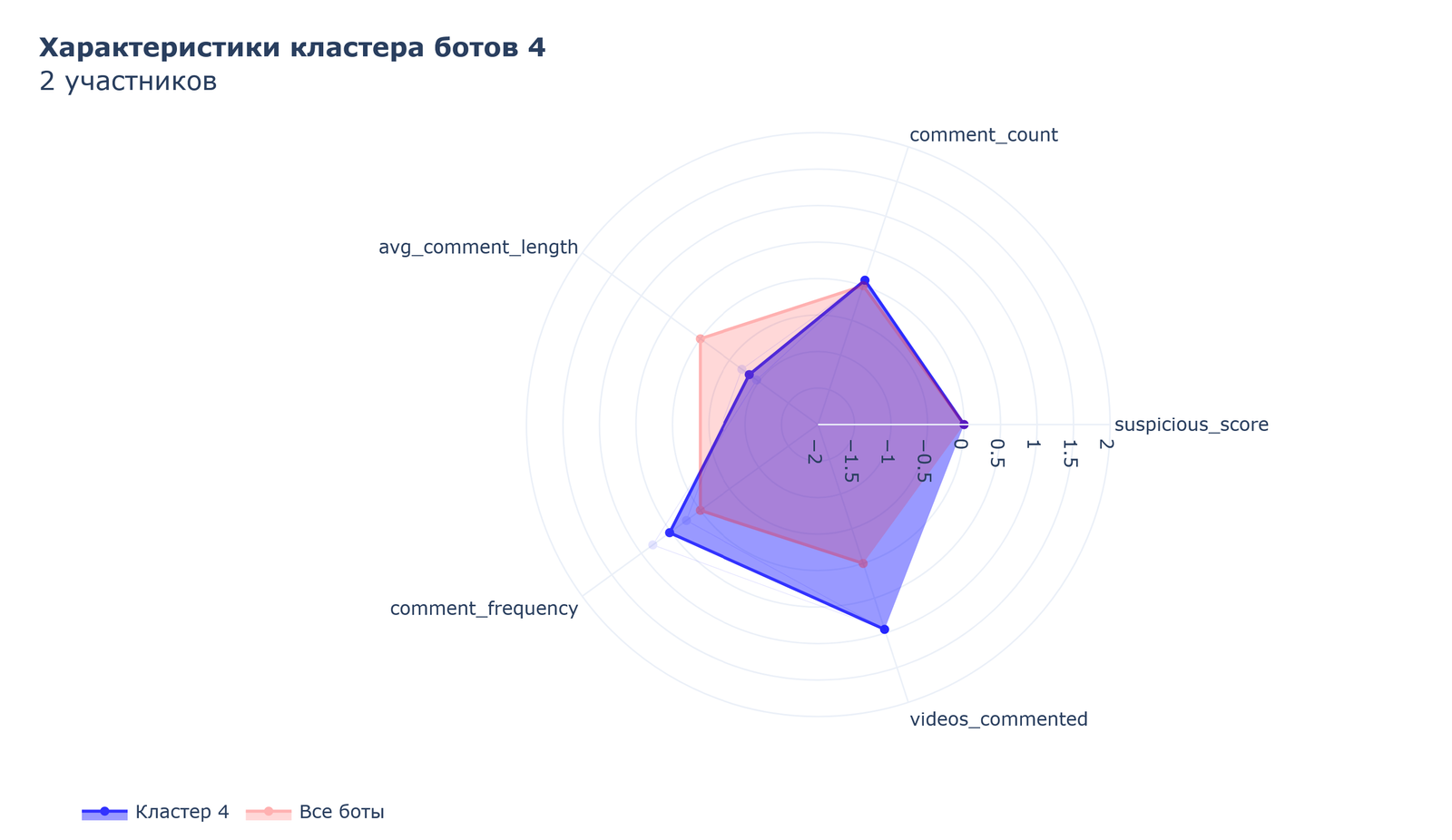
Cluster 4, also consisting of 2 participants, acts as a group of “spammers” with the most obvious signs of automation, high frequency of commenting, and significant video coverage.
Temporal Activity Patterns
Analysis of the bots’ temporal activity revealed clear patterns indicating the coordinated nature of the operation.
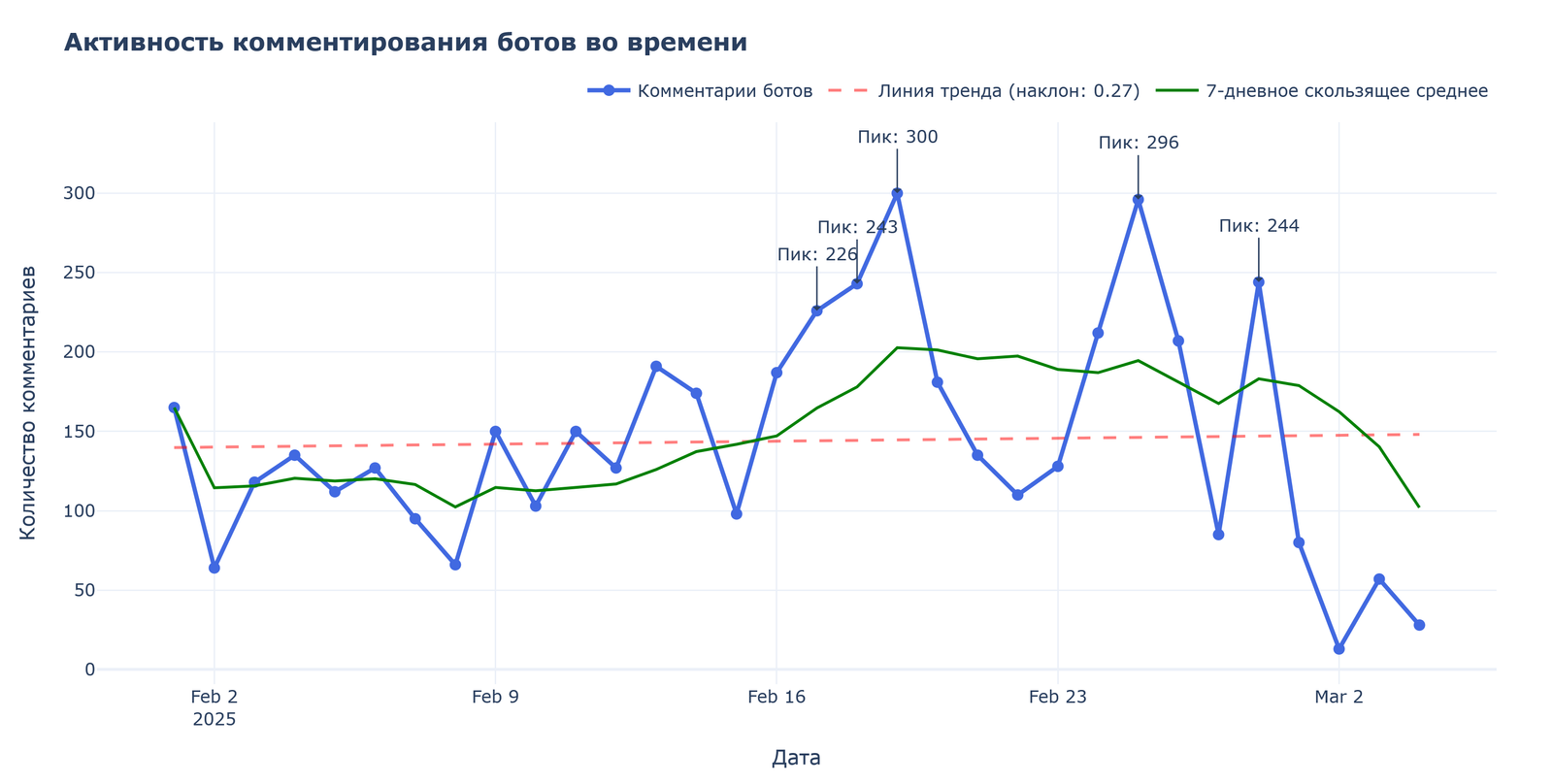
In February 2025, four main activity peaks were recorded: February 17 (226 comments), February 18 (243 comments), February 19 (300 comments, highest peak), and February 25 (296 comments). An additional peak was noted on March 1 (244 comments). After this, a sharp drop in activity was observed in early March, which may indicate the end of the information campaign or a change in tactics.
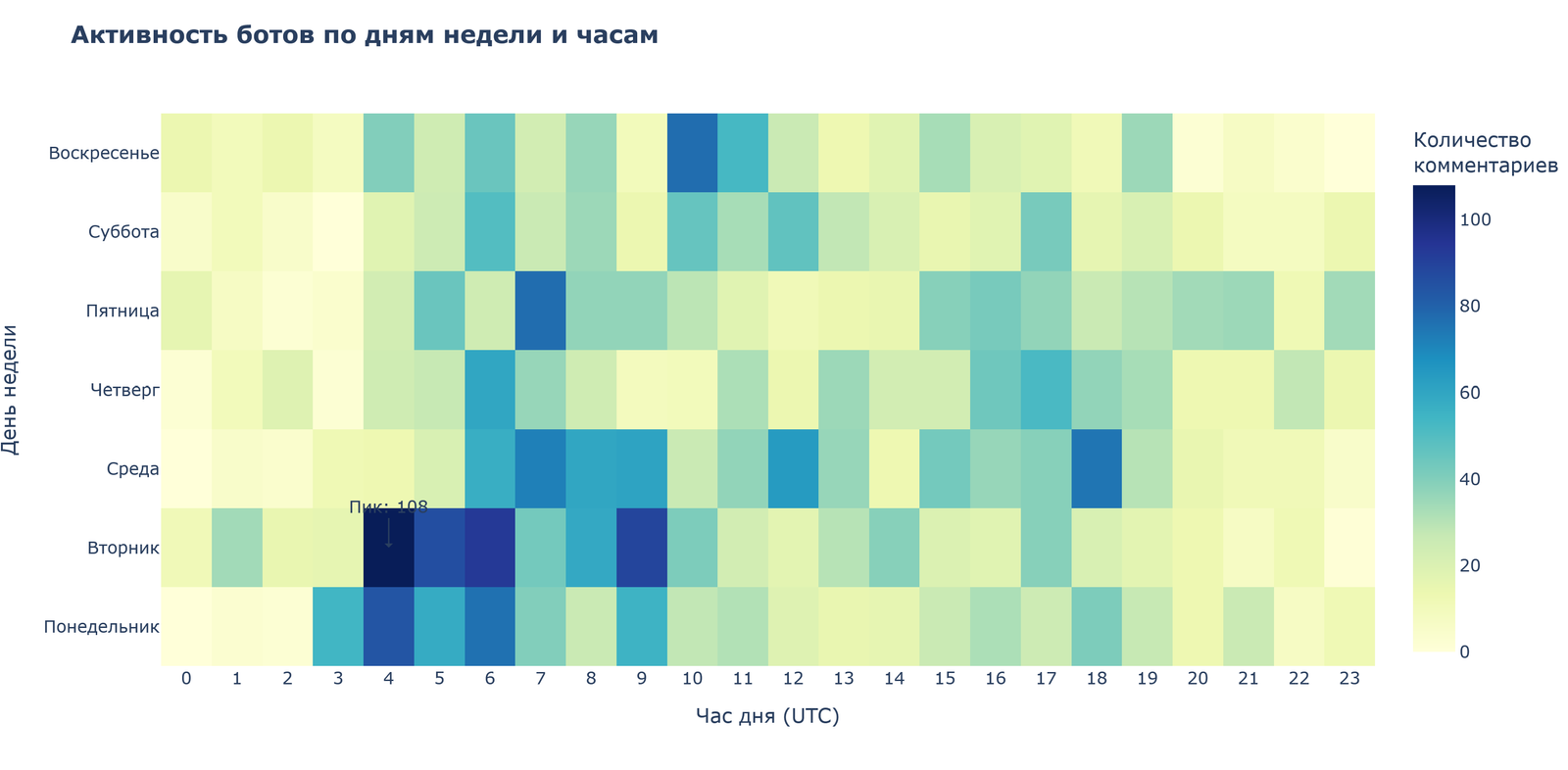
The distribution of activity by day of week and hour shows that the highest intensity occurs on Tuesday and Wednesday, as well as in the morning hours (4-7 hours UTC, which corresponds to 7-10 hours Belarusian time). Such a temporal structure indicates a professional, organized nature of the activity, likely within a standard work schedule.
Lexical Analysis
Analysis of the vocabulary used by bots showed clear thematic directions and narratives.
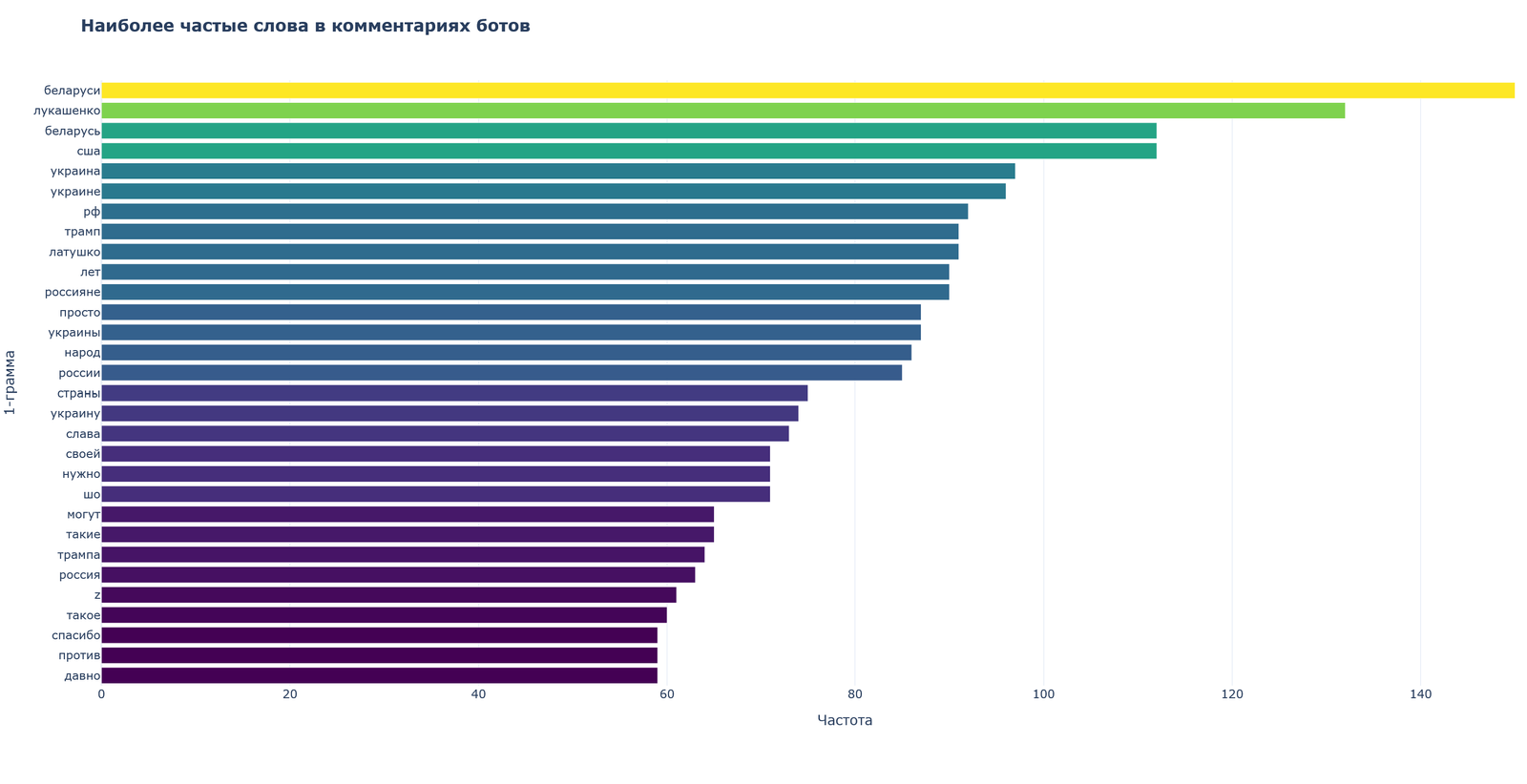
Among the most frequent words, geographic and political markers dominate, such as “belarus”, “belarus”, “lukashenko”, “usa”, “ukraine”, “rf”, indicating the geopolitical orientation of the comments.
Particularly revealing was the analysis of trigrams (sequences of three words), demonstrating the use of template constructions for mass commenting.
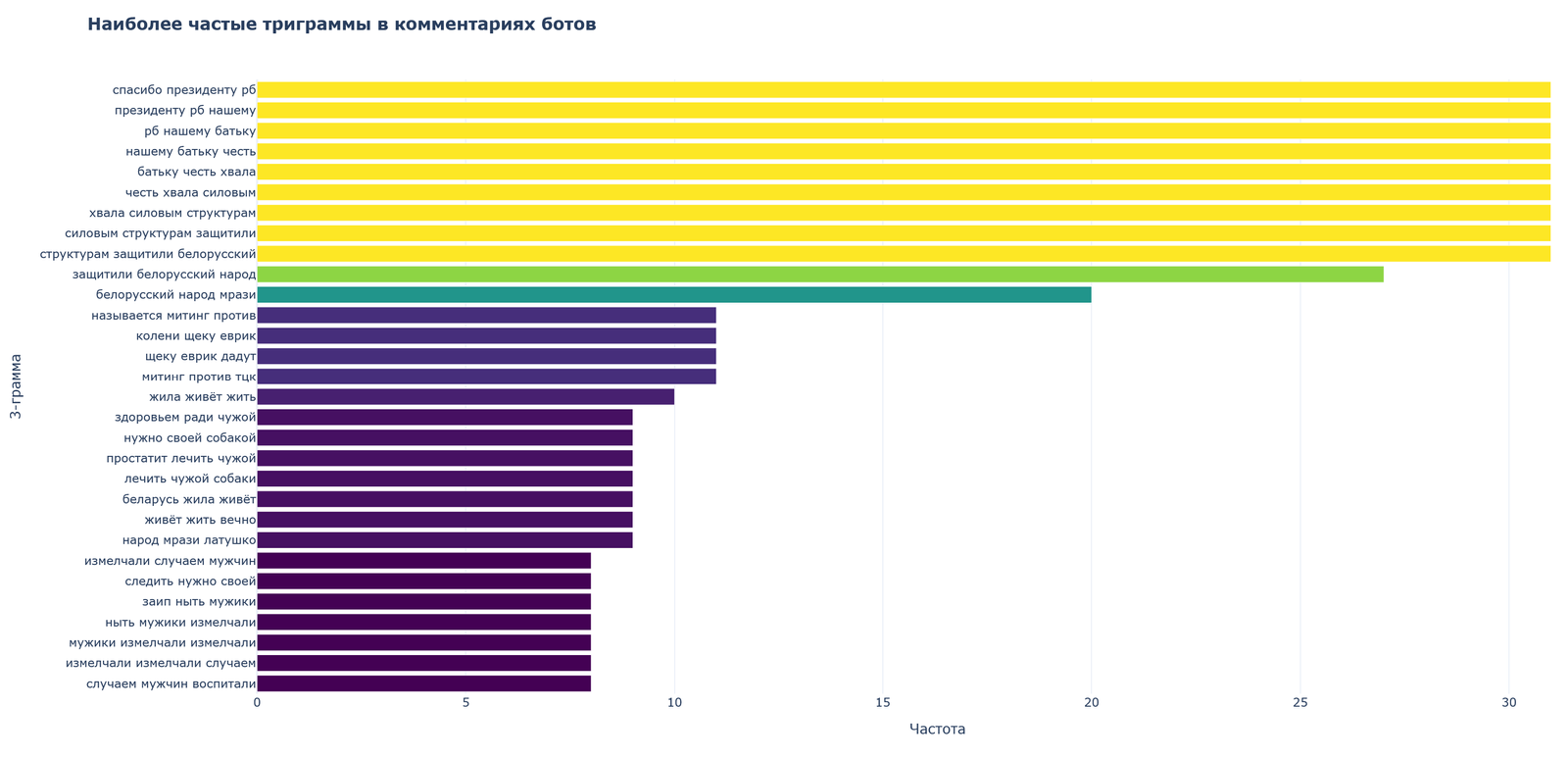
Pro-government trigrams stand out (“thanks to the president of rb”, “to the president of rb our”, “rb to our batka”), constructions supporting power structures (“glory to the power structures”, “structures protected belarusian”), anti-opposition phrases (“belarusian people prazi”, “people prazi latushko”) and patriotic statements (“belarus lived lives”, “lives live forever”).
The nature of the trigrams indicates the use of ready-made templates and phrases, which is consistent with the identified botnet structure, especially with the dominant cluster 2 (“content generators”).
Target Video Materials and Engagement Analysis
Analysis of target video materials showed that bots predominantly attack videos about civic activity. The absolute leader in the number of bot comments was the video “Belarusian woman showed an example of courage” (about 400 comments).

Significant attention is also paid to materials about international relations, such as “ARMENIAN WOMAN HOSTAGE! Lukashenko bargains with Yerevan…” and “Russia and the US voted together at the UN for the first time in…”.
Channels whose videos were most attacked in February 2025:
- Real Belarus
- Belarus Beyond MKAD
- Malanka Media
- BalaganOFF
- zhizn-malina
- Pavel Latushka
Videos about the domestic political situation are actively commented on: “Lukashenko was given a deadline!”, “DRONES ARE FALLING IN BELARUS! LUKASHENKO IS SHOCKED!”.
In-depth analysis of the relationship between engagement metrics (likes, views, comments) and bot activity revealed the strategic nature of their actions.
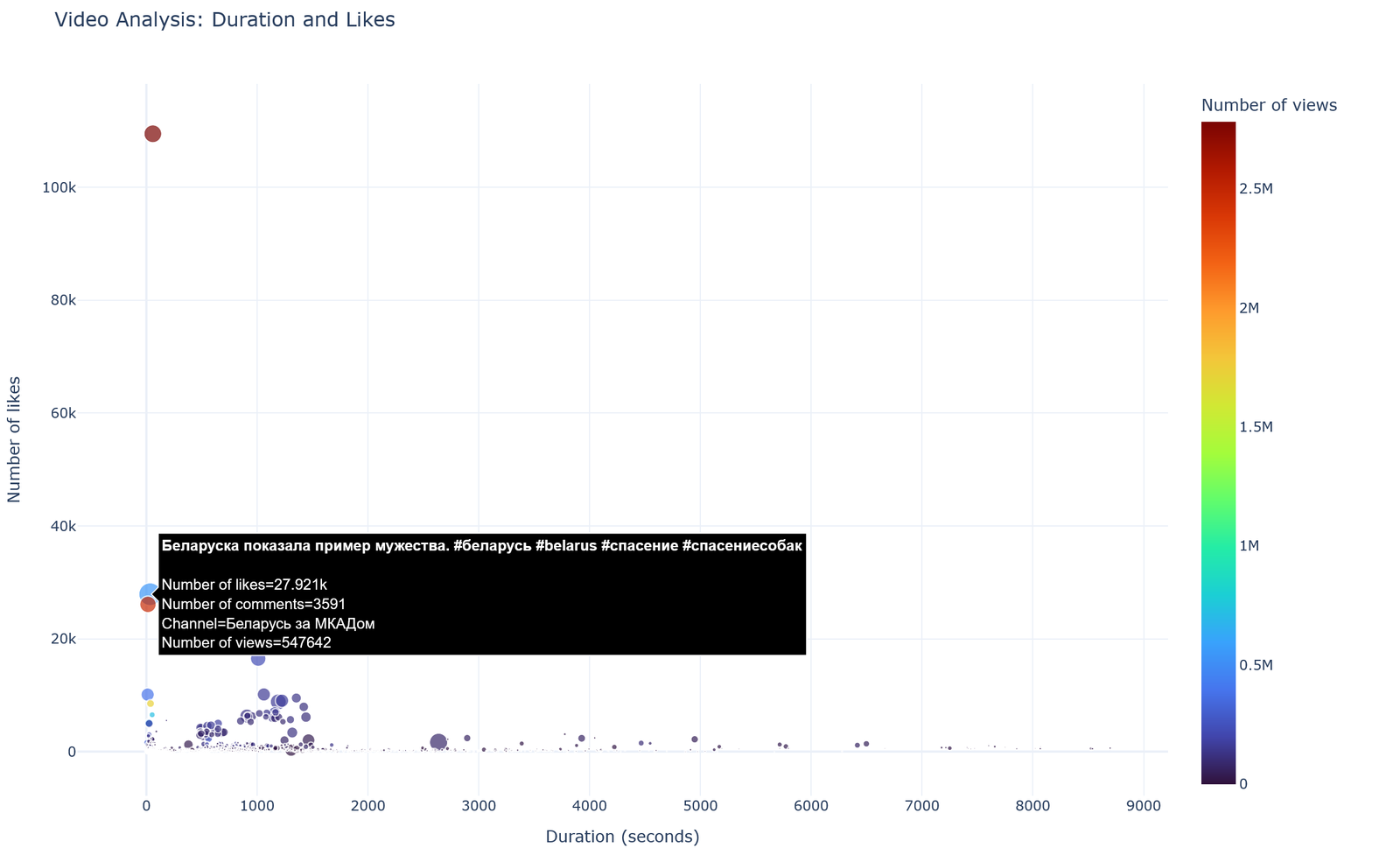
The most bot-attacked video “Belarusian woman showed an example of courage” simultaneously demonstrates exceptionally high indicators of organic engagement: 27,921 likes, 3,591 comments, and 547,642 views with a relatively short duration (less than 500 seconds). Notably, bot comments make up about 11% of the total comments on this video.
Analysis of the engagement graph, which displays video duration, number of likes, views, and comments, shows that the bulk of the content has a duration of up to 2000 seconds and relatively low engagement metrics. There is also noticeable clustering of videos lasting from 500 to 1500 seconds with increased commenting activity, which may indicate the optimal duration for stimulating discussion.
Such a targeted approach demonstrates that the bot network is primarily aimed at videos with high potential for organic distribution, especially content demonstrating examples of civic activity and resistance. The strategy involves not just random commenting, but targeted interventions in discussions that are already gaining popularity and can shape public opinion. The prevalence of emotionally colored headlines and focus on confrontational content further evidence a purposeful strategy of information influence.
Key Findings
The professional nature of the operation is manifested through the identified structure and temporal activity patterns, indicating a well-organized, professional information influence operation.
The division of roles between different bot clusters performing different functions in the overall information campaign significantly increases its effectiveness.
Bot activity is concentrated on supporting the existing regime, delegitimizing the opposition, anti-Western rhetoric, and patriotic narratives.
The presence of pronounced activity peaks and subsequent decline in activity indicates flexibility and reactivity in responding to information occasions.
The predominance of bots from cluster 2 (“content generators”) — 182 out of 201 identified bots — indicates a strategy of mass content production to create the illusion of broad support.
This research demonstrates how coordinated bot networks can systematically manipulate public opinion in social media, using various strategies and tactics. The identified patterns can be used to develop more effective methods for detecting and countering similar information operations in the future.
This publication was developed by a research team under the leadership of Mikhail Doroshevich, PhD.